
Conductive
Physical Properties
Conductive often describes materials that transmit energy, like metals in science or technology contexts.  Because gold is conductive, it's used in high-quality electronic connectors.
Because gold is conductive, it's used in high-quality electronic connectors.
Opposite Meaning
Understanding 'conductive' requires knowing its opposite, 'insulative' or 'non-conductive', which block energy flow.  Rubber boots are non-conductive, providing safety from electrical shocks.
Rubber boots are non-conductive, providing safety from electrical shocks.
Heat Context
'Conductive' can also be used when discussing how well a material transfers heat, not just electricity.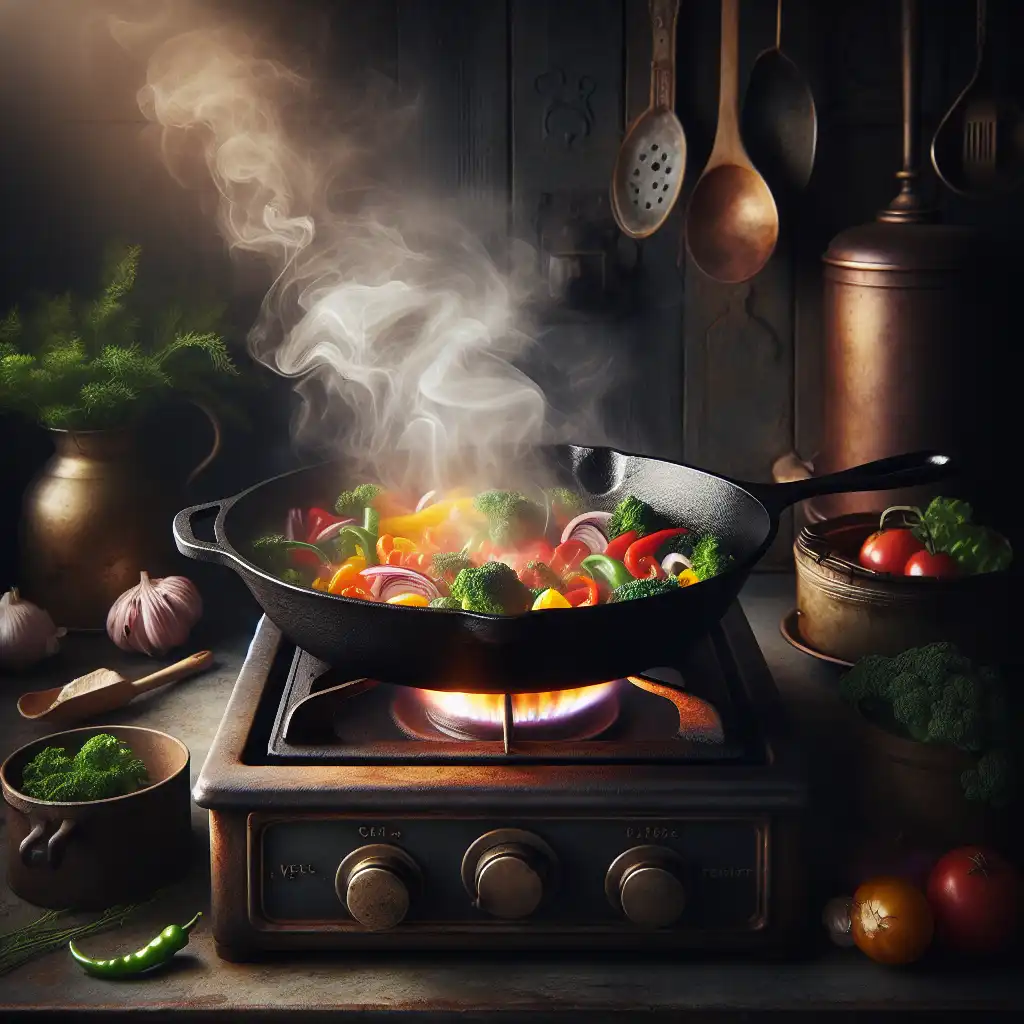  Cast iron pans are conductive, spreading the heat evenly when cooking.
Cast iron pans are conductive, spreading the heat evenly when cooking.